Suspended Refractories
Our suspended refractory designs are known for their robust construction and durability. We have designs ranging from 1.5 meters to 13.7 meters.
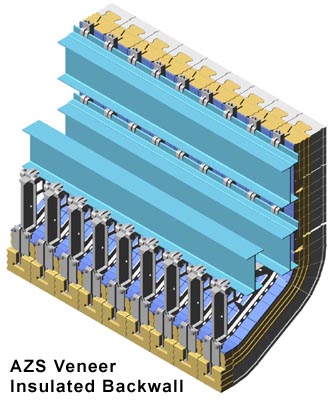
The most widely used suspended refractory is the suspended backwall.
The refractory is suspended above the doghouse by means of horizontal support steel and special castings. The suspended backwall can be configured with a wide variety of nose designs or angles from 15° - 90°. The angle on the backwall nose allows for fritting (pre-melting) in the doghouse area.
Suspended backwalls are used extensively in conjunction with blanket batch chargers due to the typically large width of the doghouse. A suspended backwall can be designed to span even the longest distances, such as those used on large float furnaces.
The refractory tiles are supported by horizontal beams and castings which are designed to move with the refractory during heat-up. This prevents any binding or unnecessary pressure between the refractories during expansion.
Our backwall tiles are fully interlocking on all four sides. This increases the integrity of the wall. In the event that a tile would break loose from a casting, it is still secured by the interlocks on all four sides.
Oxy-fuel fired funaces can suffer from increased refractory erosion through alkalai attack. Frazier-Simplex has addressed this problem in our new suspended backwall designed specifically for the higher temperature Oxy-fuel furnaces.
We have upgraded the material used in our castings to consist of high temperature stainless steel alloy. This allows us to heavily insulate the backwall without compromising the strength or integrity of the castings. This alloy will allow our castings to operate safely to 1800°F (928°C).
The Oxy-fuel insulation packages we offer range from 1/2" (13mm) thick to 2-1/2" (64mm) thick.
The Oxy-fuel suspended backwall is available in many refractory types - fused cast AZS, bonded AZS, and others.
Suspended Roofs
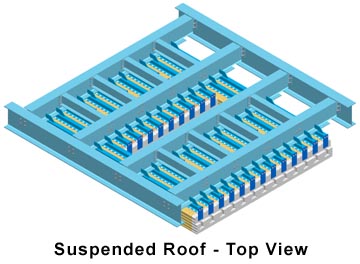
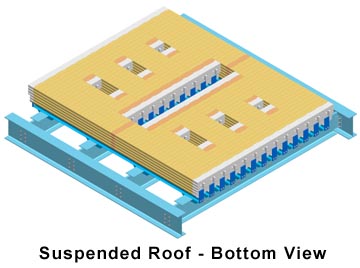
Our suspended refractories can also be utilized in a horizontal roof design. The advantages of this application with our designs include interlocking features of tiles and independent support of each tile; therefore the likelihood of failure and refractory contamination is greatly minimized.
The images below depict a cold top electric melter roof. This particular application has through the roof electrodes and a spreader to distribute the batch evenly on top of the glass surface. The image on the left shows the top support steel. The image on the right is rotated 180° to demonstrate the amount of penetrations through the roof that are capable with this type of design.